Last Updated on March 18, 2024 6:34 pm
I wish I had learned this earlier. But Linux has a simple command that allows you to time how long it takes for a command to complete. It is conveniently named time.
This is useful for basic benchmarking or troubleshooting, like copying a file from A to B.
When you use the time command, it spits out three different values: real, user, sysreal is the actual time it took for the command to processuser is the CPU time spent in user modesys is the CPU time spent in kernel mode
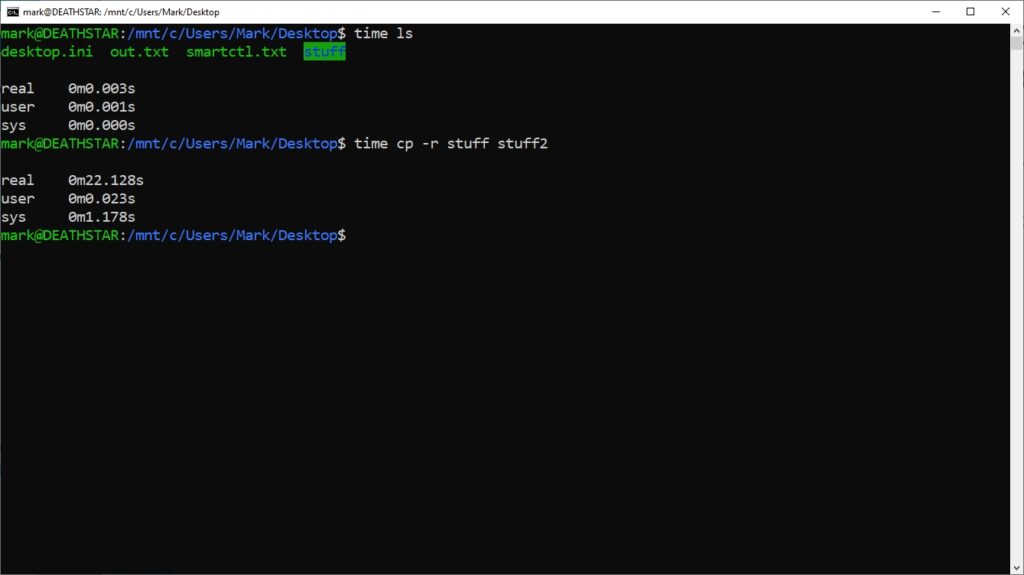
There are other options that can be used with it like -p for portable output format, -v for verbose, -o FILE to add to a file instead of console.
It can be a very useful tool for quick benchmarking and I’ve already started to use it frequently.
